Resultant Radius of Curvature of Stylet and Tube Steerable Needles
Our paper “Resultant Radius of Curvature of Stylet-and-Tube Steerable Needles Based on the Mechanical Properties of the Soft Tissue, and the Needle” is accepted to be published at the proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), which is scheduled to be held on Sun, Oct 25, 2020 – Thu, Oct 29, 2020 at Las Vegas, NV (most likely it will be virtual because of the Pandemic).
The contributors to this project are Fan Yang, and Mahdieh Babaiasl, who conducted the research under the supervision of Dr. John Swensen.

The abstract of the paper is as follows:
Steerable needles have been widely researched in recent years, and they have multiple potential roles in the medical area.
The flexibility and capability of avoiding obstacles allow the steerable needles to be applied in the biopsy, drug delivery, and other medical applications that require a high degree of freedom and control accuracy.
The radius of Curvature (ROC) of the needle while inserting in the soft tissue is an important parameter for evaluation of the efficacy, and steerability of these flexible needles.
For our Fracture-directed Stylet-and-Tube Steerable Needles, it is important to find a relationship among the resultant insertion ROC, pre-set wire shape, and the Young’s Modulus of soft tissue to characterize this class of steerable needles.
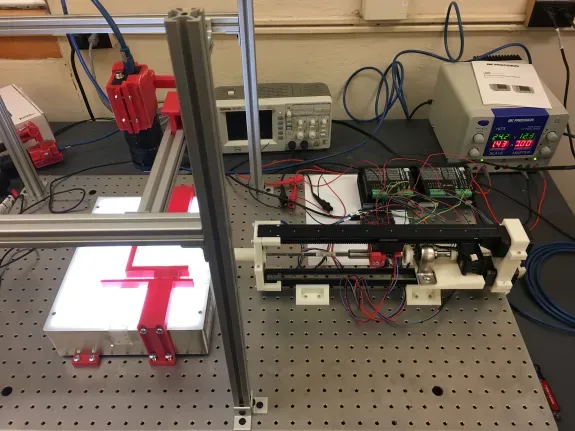
In this paper, an approach is provided for obtaining resultant ROC using stylet and tissue’s mechanical properties. A finite element analysis is also conducted to support the reliability of the model.
This work sets the foundation for other researchers to predict the insertion ROC based on the mechanical properties of the needle, and the soft tissue that is being inserted.
You can find the Materials and Codes related for the Stylet and Tube Steerable Needles in the link below:
