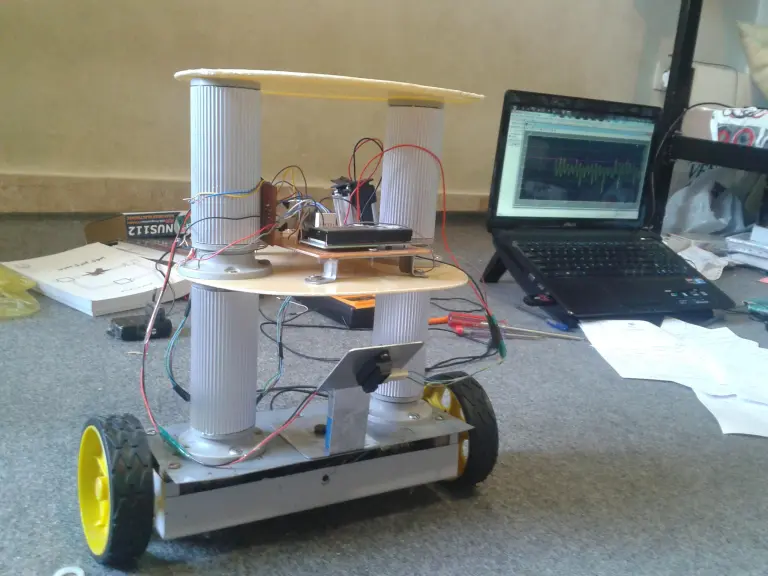
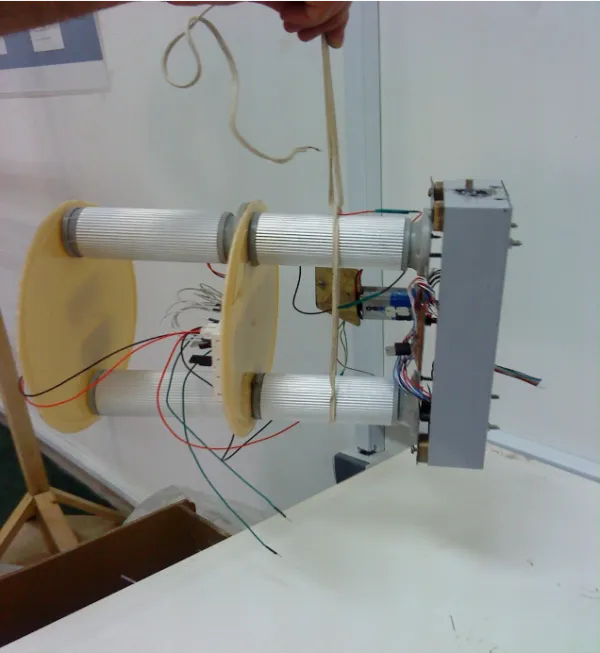
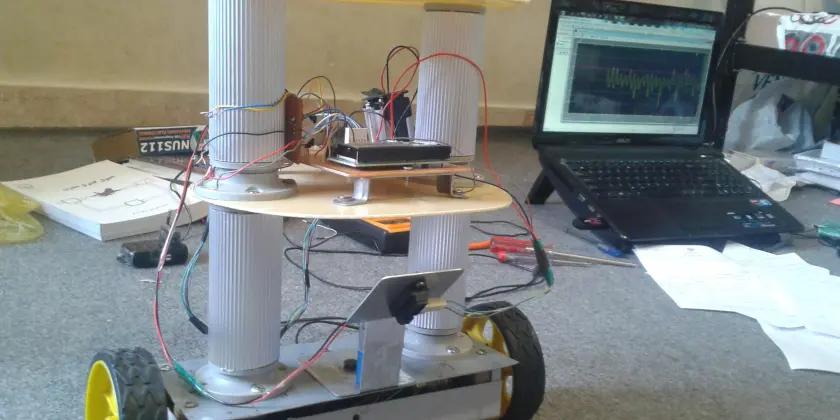
Segway Robot (Two-Wheeled Robot)

Note: Segway Robot project was done during the years 2011 – 2013 when Madi was a Master’s student.
Study on two-wheeled robots started in late 1990 in different robotic labs in different countries. The main objective is to design a balanced two-wheeled robot that has human-like abilities.
The main research challenge in these robots is the inherent instability of their dynamical system. These robots can be used as autonomous vehicles in companies, factories, or just to transport people.
Mechanical Design of Segway Robot
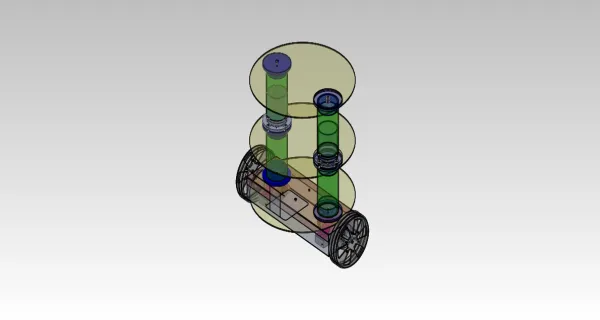
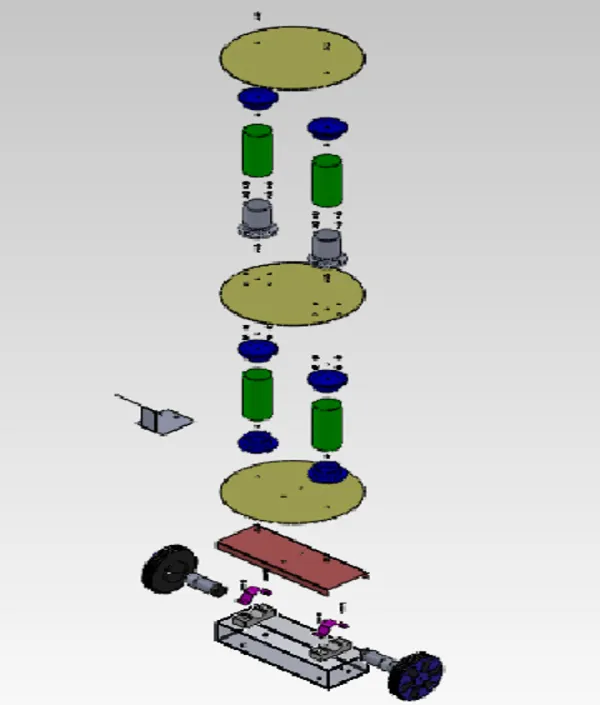
Actuator Modeling
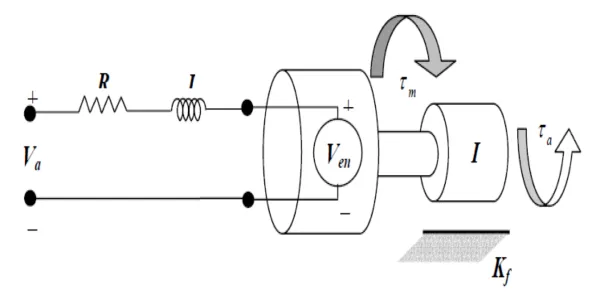
According to Kirchhoff’s law:
Newton’s Law for the shaft of the motor:
Thus:
Wheel Modeling
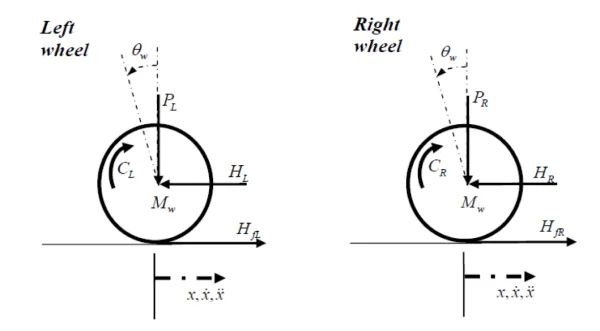
Applying Newton’s law in the x-direction and around wheel axis:
Chassis Modeling
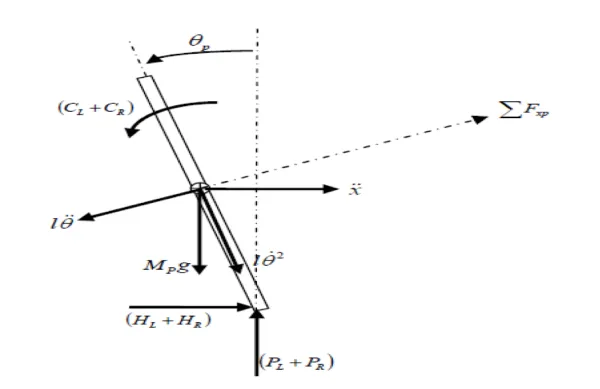
Applying Newton’s laws to the chassis’s free diagram:
Linearizing the above nonlinear equations, the state equations of the system are as follows:
Segway Robot Electronics
Motor specifications
EMG30, DC motor with gearbox and encoder, 170 rpm speed, 1.5 kg/cm torque. Motor driver is L298 IC.

Sensor Specifications
GP2D12 distance measuring sensor, 10-80 cm range, 5(v) power supply, voltage output

Designed Segway Robot Circuit in Proteus

Built Segway Robot